Liabilities Accounting Definition + Examples

It falls under the category of things you owe or borrow, including short-term loans and long-term loans. Timing differences in revenue recognition and expense recording can also create negative liabilities. Under the accrual accounting method, revenue and expenses are recorded when earned or incurred, not when cash is exchanged.
What is a Contingent Liability?
- List all your debts, their amounts, due dates, and interest rates.
- Their valuation should be consistent with the valuation of assets and expenses.
- When you make accounting judgments about liabilities, document your key assumptions so you can explain them later.
- Liabilities appear on the balance sheet, while expenses are on the income statement.
There are many different types of liabilities including accounts payable, payroll taxes payable, and bank notes. Basically, any money owed to an entity other than a company owner is listed on the balance sheet as a liability. Accounts Payable represent amounts a company owes to its Accounts Receivable Outsourcing suppliers for goods or services purchased on credit. Short-Term Notes Payable are formal written promises to pay a specific amount within one year, often bearing interest.
The importance of liabilities when acquiring or selling a company

The warranty liability may appear to be too high (or too low) at some point in time. If the liability turns out to be too low, additional expenses need to be booked. (See Dell’s 4.1 million laptop battery recall program, for example.) If the liability is too high, liability account meaning some of the expenses can be reversed. In our next lesson we’re going to define and clarify the final element of the basic accounting equation, owners equity.
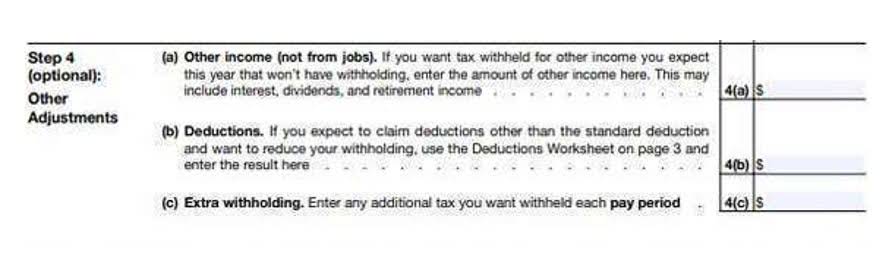
Can Liabilities be Offset Against Assets?

Errors in payroll processing significantly contribute to negative liabilities. Overestimating payroll obligations due to incorrect benefit calculations or outdated employee records can lead to this issue. Regular internal audits and reconciliations are crucial to maintaining accurate financial records.
Contingent liabilities
Bondholders, however, will require to be compensated for allowing the firm to have such an option. Therefore, the terms of the bond will include a penalty to be paid by the firm to the bondholders when the firm calls the bond. A present obligation of the entity as a result of past events, the https://fittedrims.net/bookkeeping/what-is-absorption-costing-definition-income/ settlement of which is expected to result in an outflow of the entity’s resources (payment). The debt ratio shows the percentage of a company’s assets financed through liabilities.
Managing liabilities effectively, such as loans or accounts payable, ensures smooth operations and facilitates growth. Ultimately, balancing liabilities against assets provides insight into financial stability and net worth. A liability is something that a person or company owes, usually a sum of money. Liabilities are settled over time through the transfer of economic benefits including money, goods, or services. They’re recorded on the right side of the balance sheet and include loans, accounts payable, mortgages, deferred revenues, bonds, warranties, and accrued expenses.
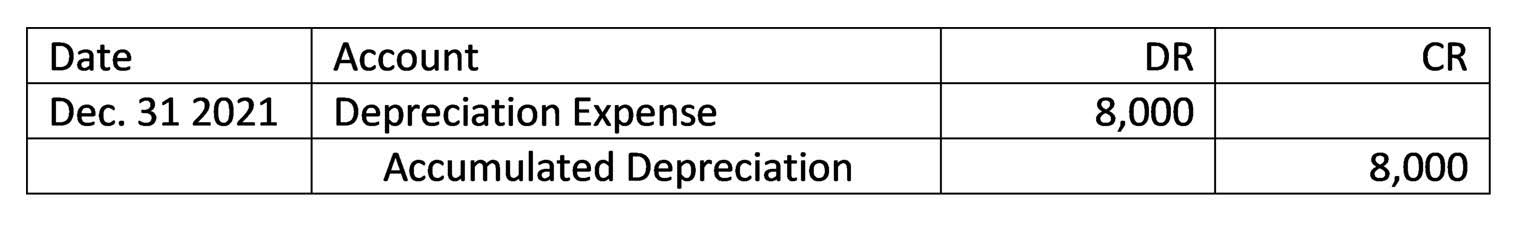
It’s particularly useful for evaluating the sustainability of long-term debt. The current ratio evaluates a company’s ability to meet short-term obligations with its current assets. These are short-term obligations that a business must settle within one year. Managing current liabilities effectively is essential to maintaining smooth day-to-day operations. Reduce unnecessary expenses, like subscriptions or luxury purchases, to save more money. The debt-to-income ratio shows how much of your income goes to paying debts.
What are liability accounts?
These are often used for significant capital expenditures or business expansion. Bonds Payable represent money borrowed by issuing debt securities to investors, with repayment scheduled over several years. Companies issue bonds to raise large sums of capital for long-term projects. Deferred Tax Liabilities arise from temporary differences between a company’s accounting profit and its taxable profit, meaning taxes are owed but will be paid in a future period. Lease Liabilities represent the present value of future lease payments for assets under finance leases. Pension Obligations are the amounts a company owes to its employees for future retirement benefits.

Leave a Reply